121/x (1) ln 121/x dy dx =y − 1 x 21/xln2 121/x ln 121/x dy dx = 12 1/x x 1SeanA(x 1,y 1),B(x 2,y 2),M(3,−1)y−→v =Since `d/(dx) ln(f(x)) = (f'(x))/f(x)` `d/(dx) sqrt(x^2 y^2) = (1/2)(x^2y^2)^(1/2)(2x) = x/sqrt(x^2y^2)` So we have `(dz)/(dx) = 1/(sqrt(x^2y^2))(x/sqrt(x^2y^2)) = x/(x^2y^2)`3/27/16 · Any real function $u(x,y)$ with continuous second partial derivatives which satisfies Laplace's equation, $$\nabla ^2u(x,y)=0$$is called a harmonic function $z(x,y)=\ln(x^2y^2)$ $$\nabla ^2 z(x,y)=\frac{\partial^2 z}{\partial x^2}\frac{\partial^2 z}{\partial y^2}$$ you can solve the above expression and it must equal to $0$ to be satisfied for the harmonic function
1 Determine The Domain For The Following Function And Draw The Graph In Xy Plane F X Y Ln X Y 2 8 Marks 2 For Z F X Y E4x2 9y14m Course Hero
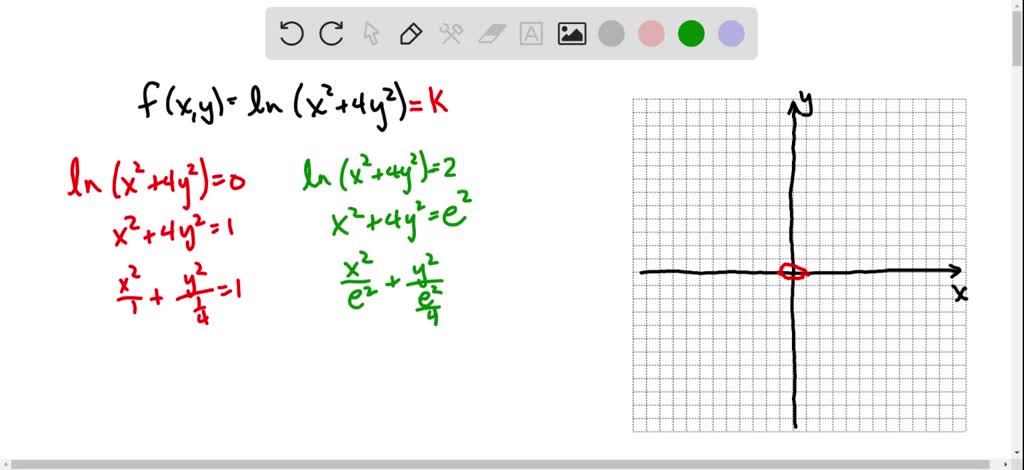
F(x y)=ln(x^2+4y^2)
F(x y)=ln(x^2+4y^2)-6/28/ · evaluate the integral y lny dy i know it's integration by parts but i get confused once you have to do it the second time Leibnitz rule (aka product rule) d(fg) = f dg g df y lny dy = dy^2/2 ln(y) y/2 dy > IntegralE y = x Then base e logarithm of x is ln(x) = log e (x) = y The e constant or Euler's number is e ≈ Ln as inverse function of exponential function The natural logarithm function ln(x) is the inverse function of the exponential function e x For x>0, f (f 1 (x)) = e ln(x) = x Or f 1 (f (x)) = ln(e x) = x Natural



Int Ln X 1 X 1 X 2 1 Dx Is Equal To A 1
1/5/14 · Beste Antwort ∂ f ( x, y) ∂ x = 2 x x 2 y 2 \frac {\partial f (x,y)} {\partial x}= \frac {2x} {x^2y^2} ∂x∂f (x,y) = x2 y22x Quotientenregel ∂ f ( x, y) ∂ x ∂ x = 2 ⋅ ( x 2 y 2) − 2 x ⋅ 2 x ( x 2 yO gráfico de f ( x, y) = g ( √ x 2 y 2) pode ser obtido rotacionando o gráfico de g no plano x z ao redor do eixo z Dada f(x, y) = 1 √16 − x2 − y2 Descreva as curvas de nível da função D = { ( x, y) 16 − x 2 − y 2 > 0 } = { ( x, y) x 2 y 2 < 16 } { z z = 1 √ 16 − x 2 − y 2, ( x, y) ∈ D }Let F(x,y) = a \ln(x^2 y^2) b Then, Using quotient rule F_x = \frac{ 2ax}{x^2 y^2} \iff F_{xx} = \frac{2a(x^2y^2)2x(2ax)}{(x^2y^2)^2} = \frac{2ay^2 2ax^2}{(x^2y^2)^2} Similarly, Let F ( x , y ) = a ln ( x 2 y 2 ) b
Free multi variable limit calculator solve multivariable limits stepbystepAnswer to Find the maximum rate of change of { f(x,y)= ln (x^2 y^2) } at the point (1, 4) and the direction in which it occurs 1) MaximumCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history
Find f_{x} and f_{y} f(x, y)=y \ln (x2 y) Join our free STEM summer bootcamps taught by experts Space is limitedMAT8 Exerc´ıcios LISTA 1 11 1 Seja f(x,y) = ln(x y −1) (a) Calcule f(1,1), f(e,1) e f(32 √ 2,−1 2) (b) Determine o dom´ınio de fL osungsvorschlag (i)Sei f R2 n(0;0) !R gegeben durch f(x;y) = ln( p x2 y2) Behauptung @ 2 @x 2 f(x;y) @ @y f(x;y) = 0 Beweis Sei x;y2R2 nf(0;0)g Aus der De nition der partiellen Ableitung (De nition 103) und den Ableitungsregeln (Lemma 104) folgt,


3 Dada La Funcion F Definida Por F X Y Ln X Y 2 1 X 2 Y 2 0 5 Determine Y Grafique El Dominio De F Ademas En El Grafique La Curva De Nivel Cero Calculo 2 Calculo Ii



Pdf Homework 2 Mth 108 Zihni Simsek Academia Edu
Skuolanet News è una testata giornalistica iscritta al Registro degli Operatori della Comunicazione Registrazione n° 792 del ©0021 Skuola Network srl Tutti i diritti riservati PI一个高数里面求函数连续性问题已知f(x)在x=1处连续,f(x)为分段函数,当X0时,ln(bx^2),求a,b答案显 1年前 3个回答 你能帮帮他们吗Subject to the constraint 2x2 (y 1)2 18 Solution We check for the critical points in the interior f x = 2x;f y = 2(y1) =)(0;



Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange



Solved X Ln Y Y Ln X 2 Ln Y X Ln X Y 2 Ln X 2 Y Chegg Com
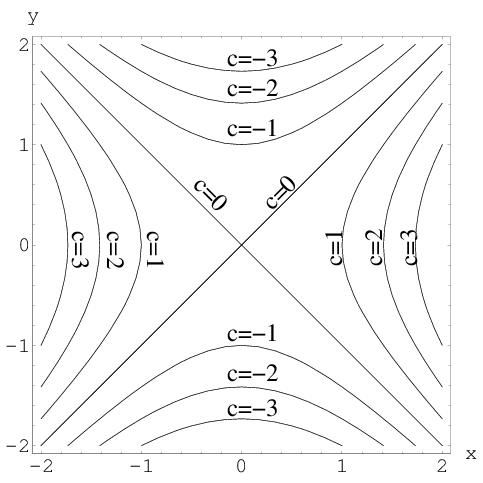
Integrate F(x,y) = Ln(x^2y^2)/sqrt{x^2y^2} Over The Region 1 Leq X^2y^2 Leq E^{10}The first derivative of mathz/math with respect to mathx/math is math\frac {\partial z}{\partial x}=\frac {2x}{x^2y^2}/math The second derivative is11/8/12 · multivariable limit of (x,y)>(1,0) of ln(1y^2/x^2xy)) Homework Statement limit of (x,y)>(1,0) of ln(1y^2/x^2xy)) Find the limit, if it exists, or show that the limit does not exist Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution so i have lim(x,y)>(1,0)



Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download



Natural Logarithm Wikipedia
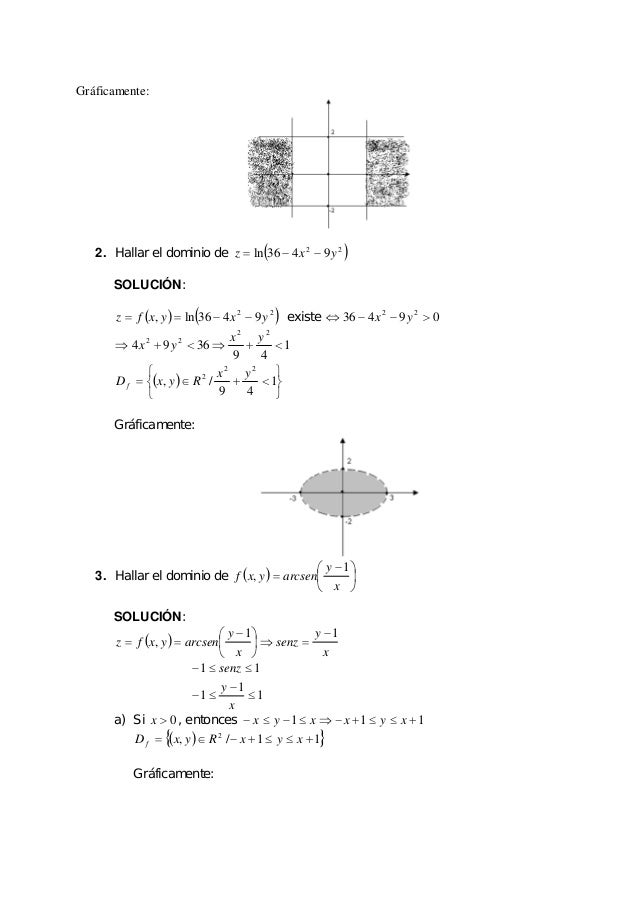
F(x;y)= x2 x2 y2 RESOLUCIÓN La función f(x;y) es una función racional, esto es, el cociente de dos polinomios Al ser los polinomios funciones continuas, utilizando la propiedad 4 anterior podemos garantizar que f(x;y) es continua salvo quizás en aquellos puntos que anulen el denominador x2 y2 Ahora bien, x2 y2 =0 8 >> < >> x =0 y =0A The given function is f(x,y)=ey in the interval x belongs to 0,8 and y belongs to 0,ln2 question_answer Q The region is formed by the graphs of y 4x and y 12xCreate your account View this answer Given that f(x, y) = ln(1x2y2) f ( x, y) = ln ( 1 x 2 y 2) Partially differentiating with respect to x we obtain {eq}\displaystyle See full


Logarithms
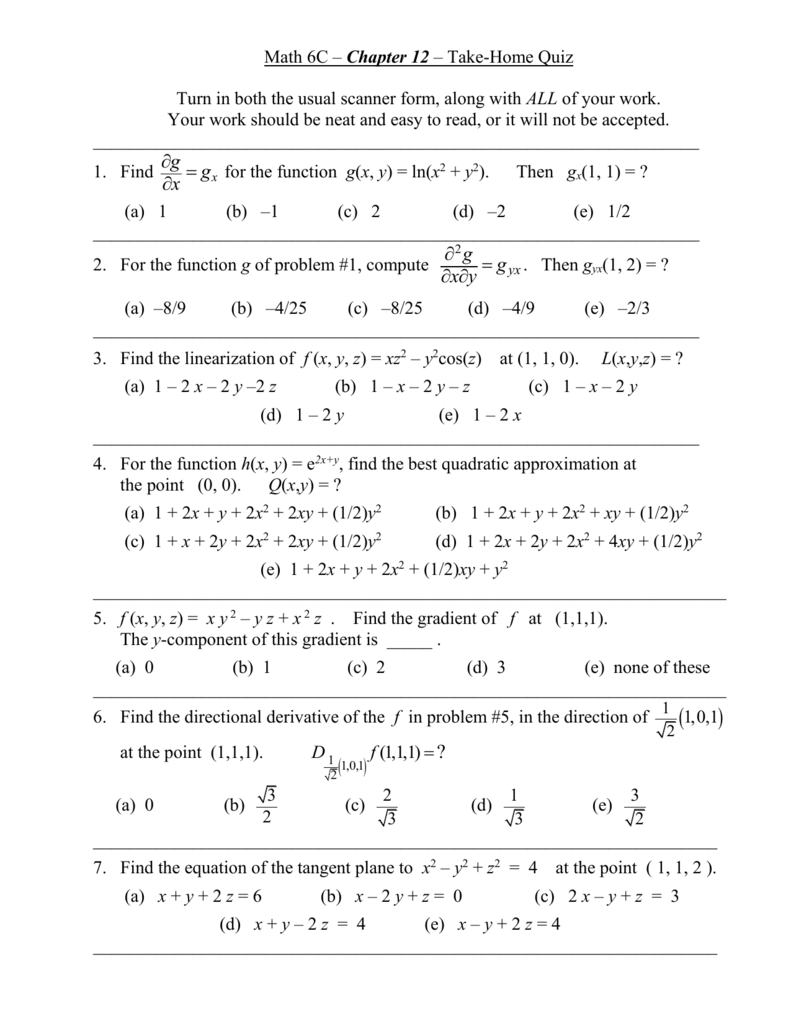


Math 6c Chapter 12 Quiz
(x,y)→(1,0) ln 1y2 x2 xy Since the natural log function is continuous on its domain, we have lim (x,y)→(1,0) ln 1y 2 x2 xy = ln lim (x,y)→(1,0) 1y x2 xy , provided the limit on the right exists and is bigger than 0 The numerator and denominator of theGrafico de´ f(x;y) = xy x 2y Repare neste ´ultimo gr ´afico a descontinuidade em (0;0) indo pelo caminho x = y, a func¸˜ao fica constante igual a 1 2 (em azul), logo tende a 1 2 Pelo caminho x = y, ela fica constante igual a 1 2 (em vermelho) e tende a esse valor1/5/18 · wie berechne ich die partielle Ableitung 1 Ordnung von der Gleichung f(x,y)=ln(y2 √(x2 y2))



Derivasjon Av Ln X


Solved Draw A Contour Map Of The Function Showing
2/16/16 · Qual a derivada parcial da f(x,y)=y^2*ln(x^2 y^2) 1 Ver a resposta Kassandra16 está aguardando sua ajuda Inclua sua resposta e ganhe pontos carlosmath carlosmath ===== Novas perguntas de Matemática 1)Encontre o valor de 40 2 – 2269 2 2) Solucione esta sentença 199² – 1² 3)Solucione esta sentença 343² – 342² 4)ACalcule as derivadas parciais de $s = f(x,y,z,w)$ dada por $s = xw \ln{(x^2 y^2 z^2 w^2)}$1) is a critical point The second derivative test f xx = 2;f yy = 2;f xy = 0 shows this a local minimum with



Natural Logarithm Wikipedia



Find The Critical Point Of The Function F X Y 28x 4y 2 Ln X Y Then Use The Critical Point Of The Function To Classify It Study Com
1/26/15 · This video illustrates the tangent line to the 3D surface to illustrate the meaning of the value of a directional derivativewebsite http//mathispower4ucom#f(x,y) = g(r)# where #r = sqrt(x^2y^2)# è il raggio polare In realtà, #g(r) = ln(r^2) = 2 ln(r)# Quindi, traccia il grafico della curva dell'equazione #z = 2ln(x)# Il #xOz# aereo Ottieni Infine, ruota questa curva attorno al #Oz# asse Hai capito #mathcal(S)#3 Como los límites no coinciden, no existe el límite de la función en ¯0 36 l´ım (x,y)→(0,0) x 2y2 ln(x2 y2) Pasando a coordenadas polares, tenemos l´ım


1 Determine The Domain For The Following Function And Draw The Graph In Xy Plane F X Y Ln X Y 2 8 Marks 2 For Z F X Y E4x2 9y14m Course Hero


How To Solve This Differential Equation X 3 Y X Y 2 Ln X Dy Dx 0 Which Is Exact Quora
Question from anu, a student the question says we have to find the points in the plane where the function is continuous f (x,y)=ln (x^2y^2) here we aren't given a particular point (x,y) where we have to check a function's continuity1 resposta (s) Contém resposta de Especialista Para resolver este problema, devemos colocar em prática nosso conhecimento sobre Cálculo Diferencial e Integral Dada a função \ (f (x,y)=\ln (\sqrt {x^2y^2})\), queremos mostrar que ela satisfaz a Equação Bidimensional de Laplace, exposta abaixo Para tanto, precisamos calcular as derivadasSee the answer Find the gradient of f(x,y)=ln(x^2y^2) Expert Answer 94% (17 ratings) When you take the gradient of a function you will get a vector You need to


Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation



Find The Local Linear Approximation L To The Function F X Y Ln Xy At The Point P 1 2 Compare The Brainly In
(c) f(x;y) = ln(x2 y2) Solution x2 y2 > 0 is the domain This consists of all points in the plane except (0;0) This is an open set The range of the function is (1 ;1) Here is a skecth of the level curves f = 1, f = 0, and f = 1This equation into two functions, f(x,y) = p 4− x2 −y2 and f(x,y) = − p 4− x2 −y2, representing the upper and lower hemispheres Each of these is an example of a function with a restricted domain only certain values of x and y make sense (namely, those for which x2 y2 ≤ 4) and the graphs of these functions are limited to a smallSeja f(x, y) = ln(x^2 y^2 4) É correto afirmar que o domínio dessa função é a) A parte interna e a borda de um de círculo de raio unitário b) A parte interior de um cone centrado na origem c) A parte superior externa de uma parábola com concavidade positiva d) A parte superior interna de uma parábola com concavidade negativa
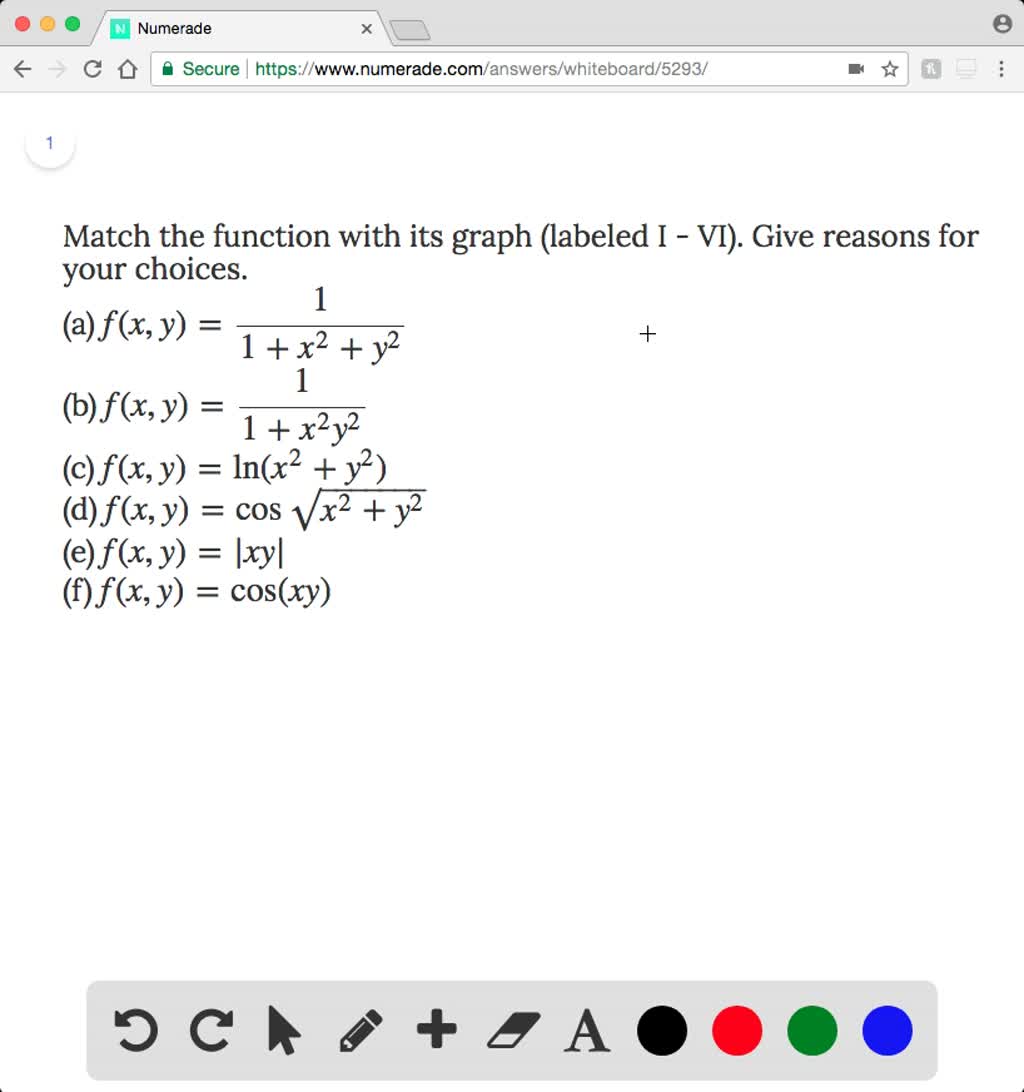


Solved Match The Function With Its Graph Labeled
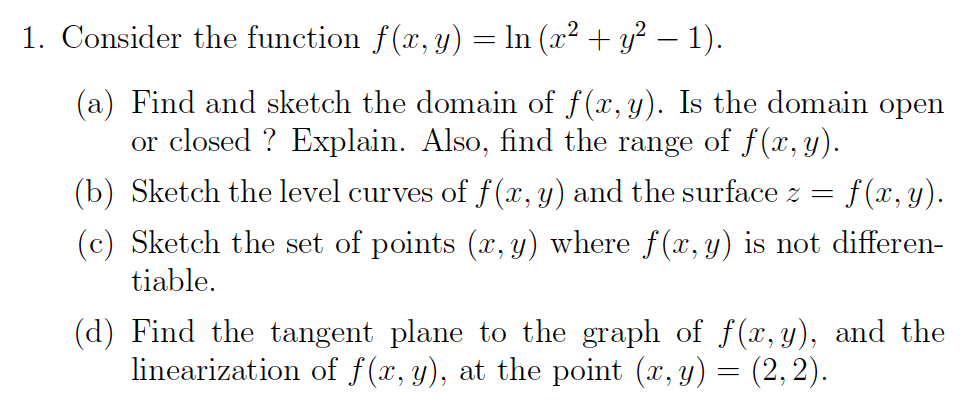


Solved Consider The Function F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 1 Chegg Com
12/21/ · The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by MindTouch ® and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers ,9/14/17 · Method 3 Implicit Function Theorem Putting F (x,y) = ln(x2 y2) − y We have ∂F ∂x = 2x x2 y2 ∂F ∂y = 2y x2 y2 −1 = − x2 y2 −2y x2 y2 Then dy dx = − ∂F ∂x ∂F ∂y = − 2x x2y2 − x2y2−2y x2y24/19/18 · (xy)²≤2(x²y²) 0=lim√(2u)lnu≤lim≤lim√(2u)lnu=0 夹逼准则,lim=0


Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation



Matlab Tutorial
3 Dada la función f, definida por f(x,y) = ln(xy^2)/(1(x^2y^2)^05) Determine y grafique el dominio de f, además en él grafique la curva de nivel cero Curso Cálculo 2 (Cálculo ii Ing) de la universidad Universidad Peruana de Ciencias AplicadasLet f(x,y)=1/(x^2y^2) for (x,y)\neq 0 Determine whether f is integrable over U0 and over \mathbb{R}^2\bar{U};The feasible region for #f(x,y)= arcsin(x^2y^25)Ln(x2y1)# is given by #1 le x^2y^25 nn x^2y^25 le 1 nn x 2y 1 > 0# which corresponds to the region plotted in light blue



Determine Whether The Given Function Is Homogeneous If So State The Degree Of Homogeneity Math Ln X 2 2 Ln Y Math Homework Help And Answers Slader



Matlab Tutorial
· for the domain of ln (x^2 y^2 ) , it it given in my notes that the ans is x ≠ 0 and y ≠ 0 IMO , it's wrong to give x ≠ 0 and y ≠ 0 , because the meaning of x ≠ 0 and y ≠ 0 is that x and y cant be 0 all the times so just leave the ans (x^2 y^2 ) > 0 , will do ?Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyQuestion Find The Gradient Of F(x,y)=ln(x^2y^2) This problem has been solved!



Consider The Function F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 3 Compute The Partial Derivatives Of The First And Second Order Mathematics Stack Exchange
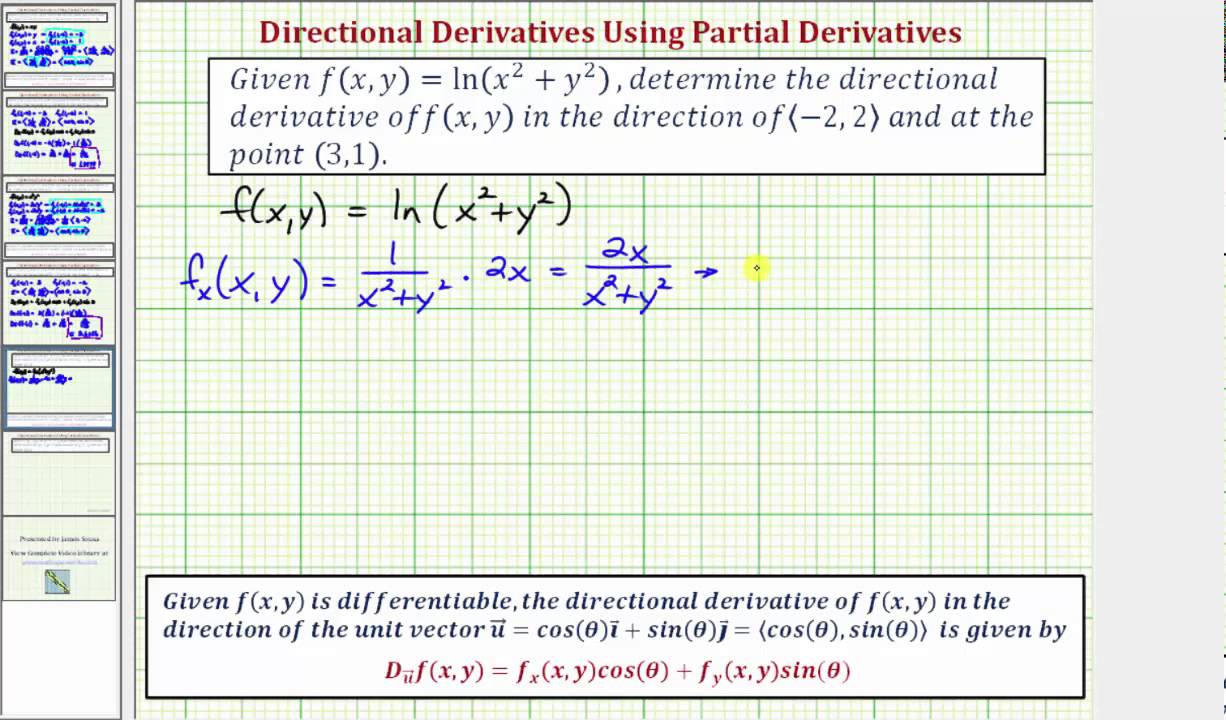


Ex 3 Find A Value Of A Directional Derivative F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube


Draw The Graph Of F X Ln 1 Ln X Find The Point Of Inflect


Natural Logarithm Rules Ln X Rules



Solved Find And Sketch The Domain Of Each Function A F Chegg Com
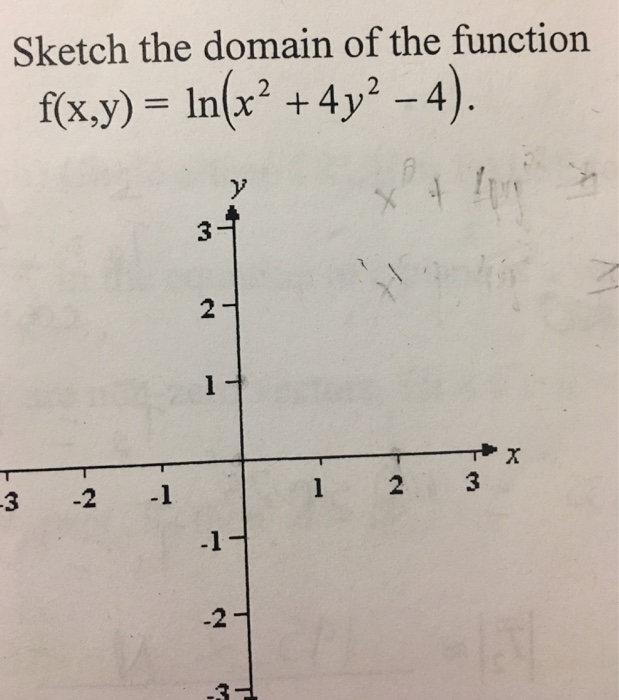


Solved Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Ln X Chegg Com



Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download


Funciones Reales Variables


Level Set Examples Math Insight


Ejercicios 4 Cvv Holi Studocu



Answered 53 58 Find All The Second Partial Bartleby



Solved Find And Sketch The Domain For Each Functi



Int Ln X 1 X 1 X 2 1 Dx Is Equal To A 1



Solved Find And Sketch The Domain For Each Function F X Chegg Com



Answered 54 Y Ln X Cos Cos X 3d Bartleby
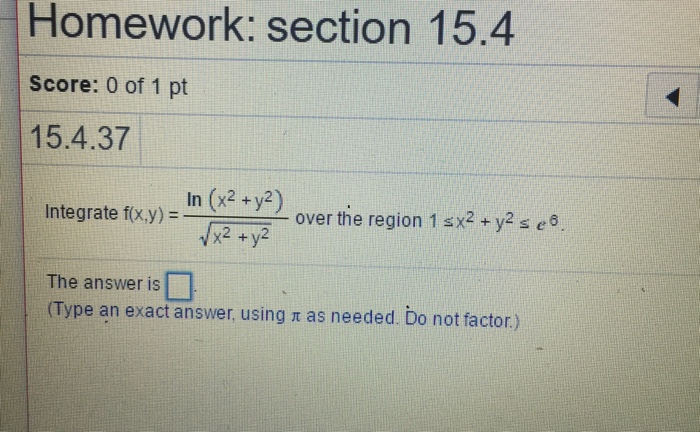


Solved Integral F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Squareroot X 2 Chegg Com



Worksheet3 Sol Pdf Vv255 Dr Jing Liu Exercise 3 Question1 1 Points P If F X Y X Y X2 Y 2 Find Fx0 3 4 Fy0 0 5 Solution 1m We Have 2x P 1 2 X2 Y 2 Course Hero


Ex 3 Find A Value Of A Directional Derivative F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Math Help From Arithmetic Through Calculus And Beyond



Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Frac Ln X 2 Y 2 4 Sqrt 4 X 2 Sqrt 4 Y 2 Study Com



14 1 Functions Of Several Variables Mathematics Libretexts



Max And Min X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange


Contour Map Of The Function Showing Several Level Curves Physics Forums


How Do You Find The Volume Bounded By Y Ln X And The Lines Y 0 X 2 Revolved About The Y Axis Socratic


If Ln X Y Ln X Ln Y What Are The Values Of X And Y Quora



Compute The Divergence Of The Vector Field F X Y Z Ln X 2 Y 2 I Math Videos F X Computer


If Ln X Y Ln X Ln Y What Are The Values Of X And Y Quora



First Order Partial Derivatives Of F X Y Ln X 4 Y 4 Youtube
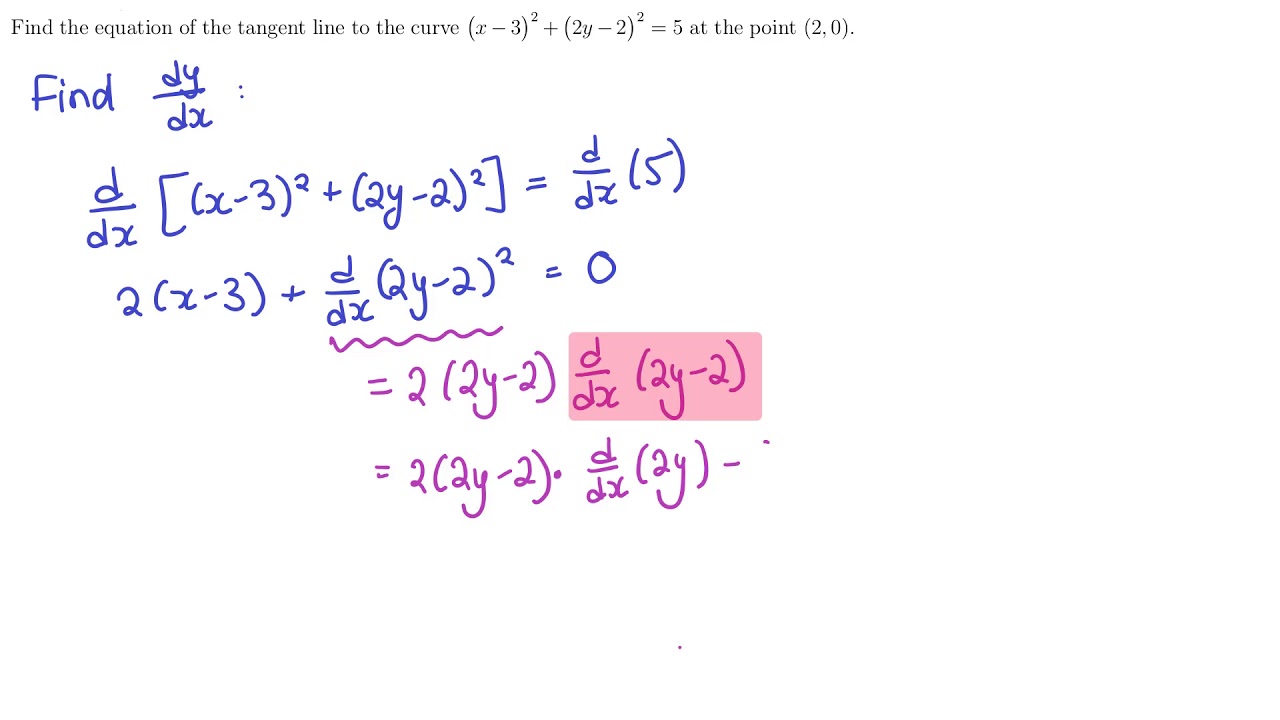


Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation



Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
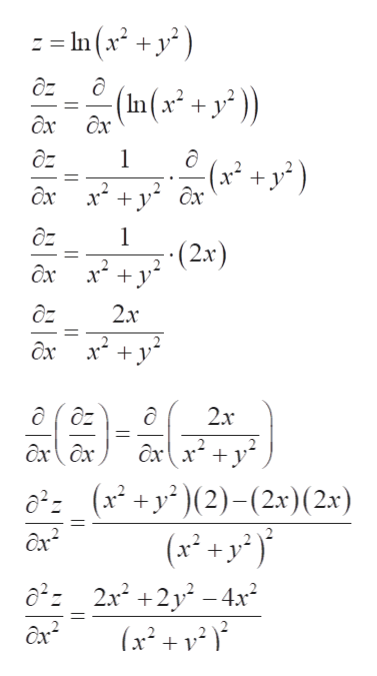


Answered Show That F X Y Ln X2 Y2 Solves Bartleby


Logarithmic And Exponential Functions Topics In Precalculus



Ejercicios De Calculo Vectorial Pagina 2 Monografias Com


Level Surfaces



Solutions F X 6x 2 6xy 24x F Y 3x 2 6y To Find The Critical Points We Solve Pdf Free Download
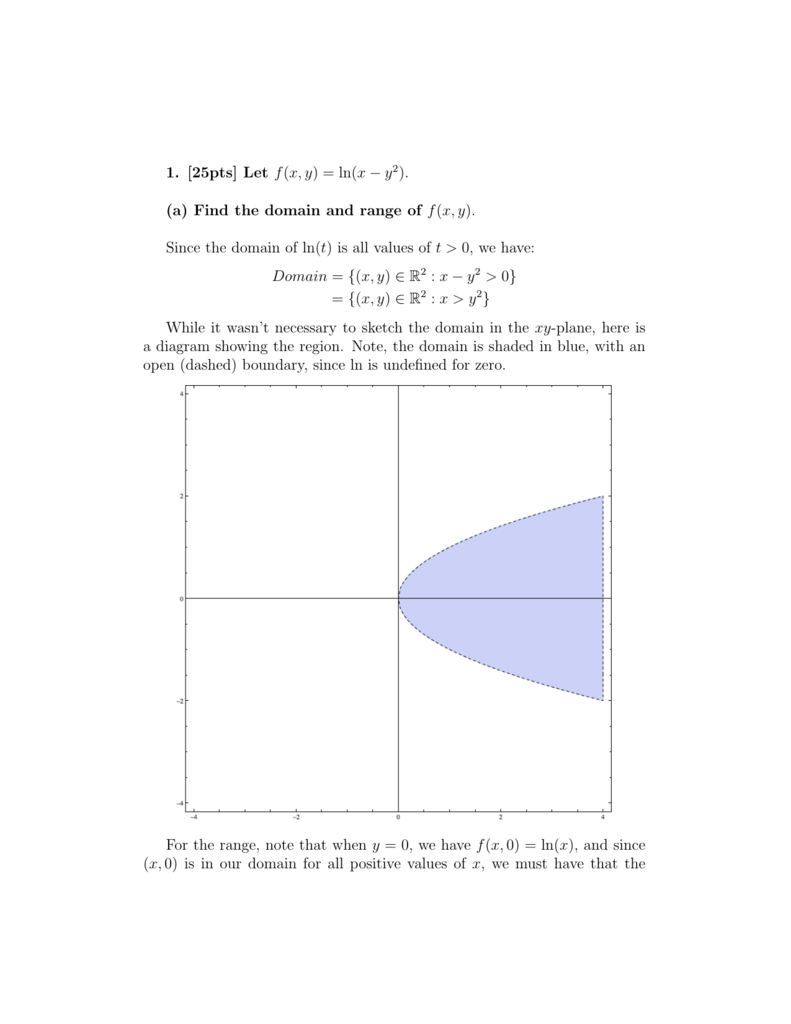


1 25pts Let F X Y Ln X Y 2 A Find The Domain And Range Of F X


5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function



First Order Partial Derivatives Of F X Y Ln X 4 Y 4 Partial Derivative Math Videos Maths Exam


Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Ln 9 X 2 9y 2 Homework Help And Answers Slader


7 1 The Natural Logarithm Function


How To Find The Domain And Range Of F X Y Ln Xy 2 Youtube
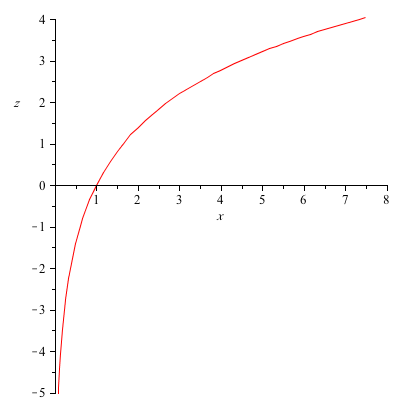


How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic



Ejercicios De Calculo Vectorial Pagina 2 Monografias Com
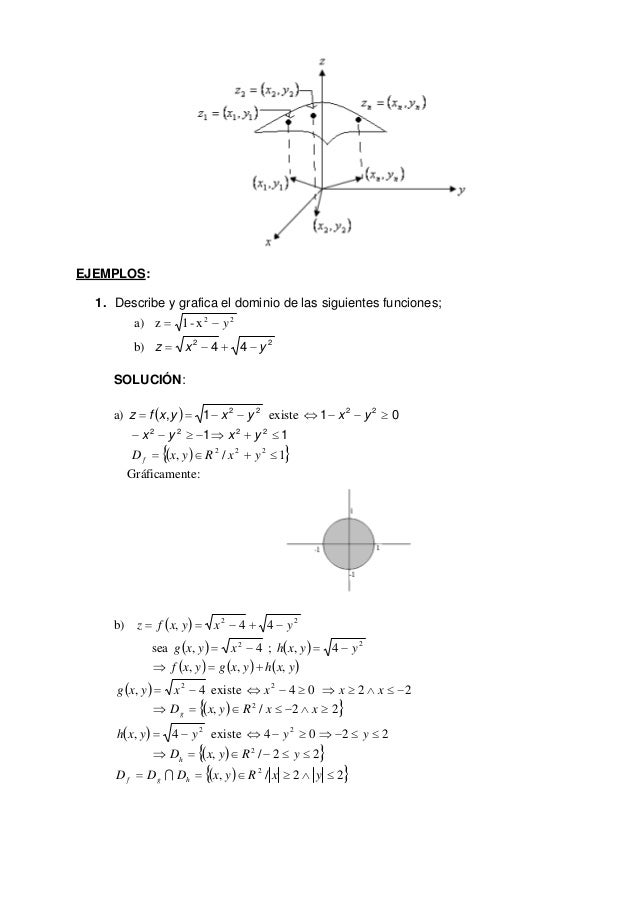


Funciones Reales Variables


Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy


7 1 The Natural Logarithm Function
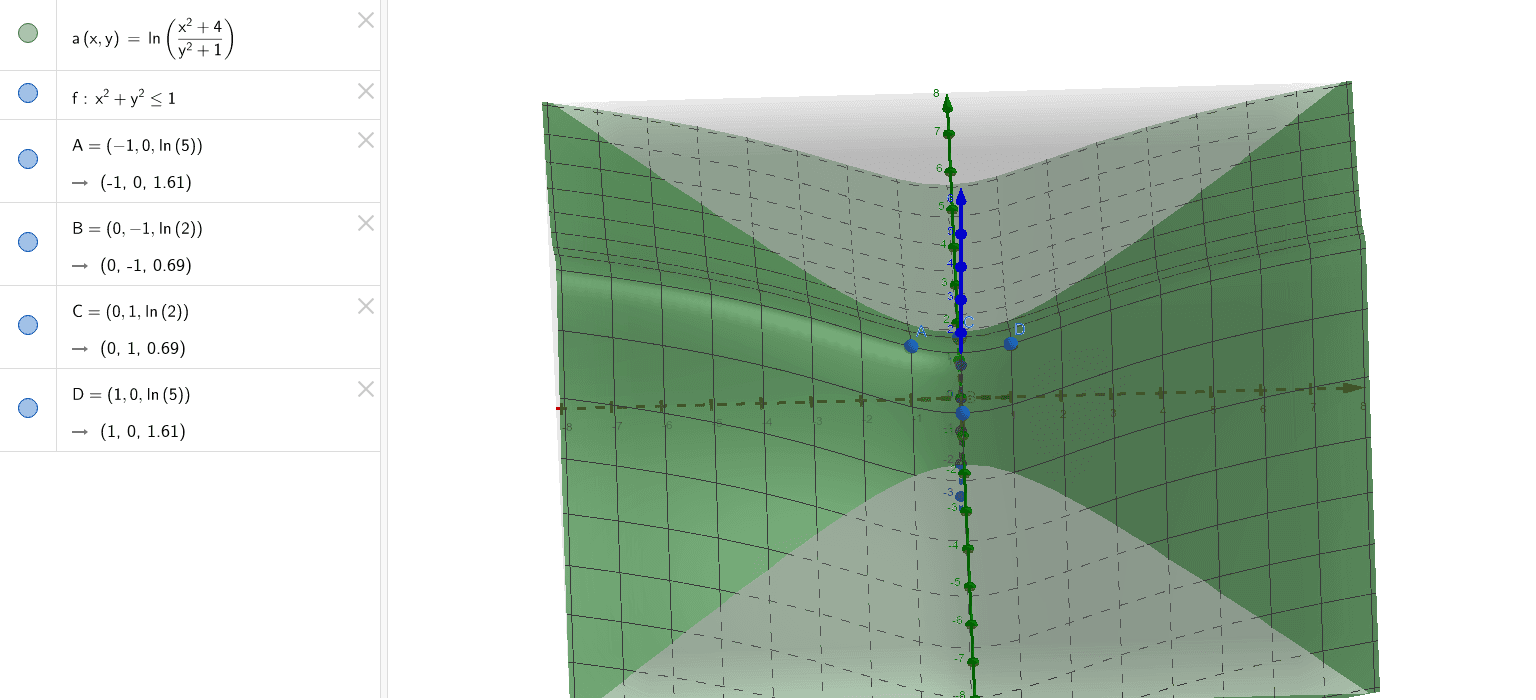


Max Min Inside X 2 Y 2 1 Of F X Y Ln X 2 4 Y 2 1 Geogebra



Partial Differentiation And Multiple Integrals Pdf Free Download
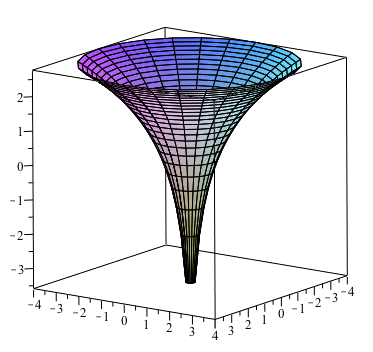


How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic
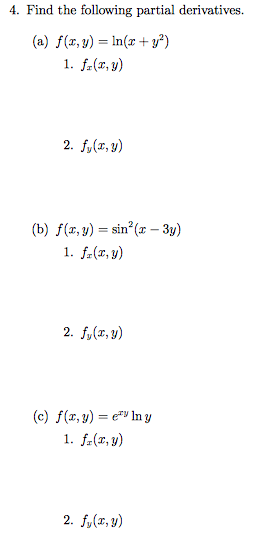


Solved 4 Find The Following Partial Derivatives A F X Chegg Com


Graphs E X And Ln X Geogebra
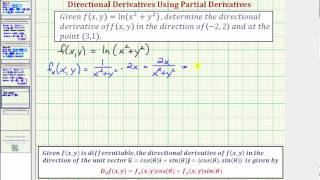


Ex 3 Find A Value Of A Directional Derivative F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube



Solved 1 Let F X Y Ln X Y 1 A Evaluate F E Chegg Com


How Do You See It The Figure Shows The Graph Of F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 From The Graph Does It


Y Ln X 14



Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Z Ln 16 4x 2 4y 2 Z 2 Youtube


What Is The Domain Of F X Y Ln Xy Quora


5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function


Partial Derivatives
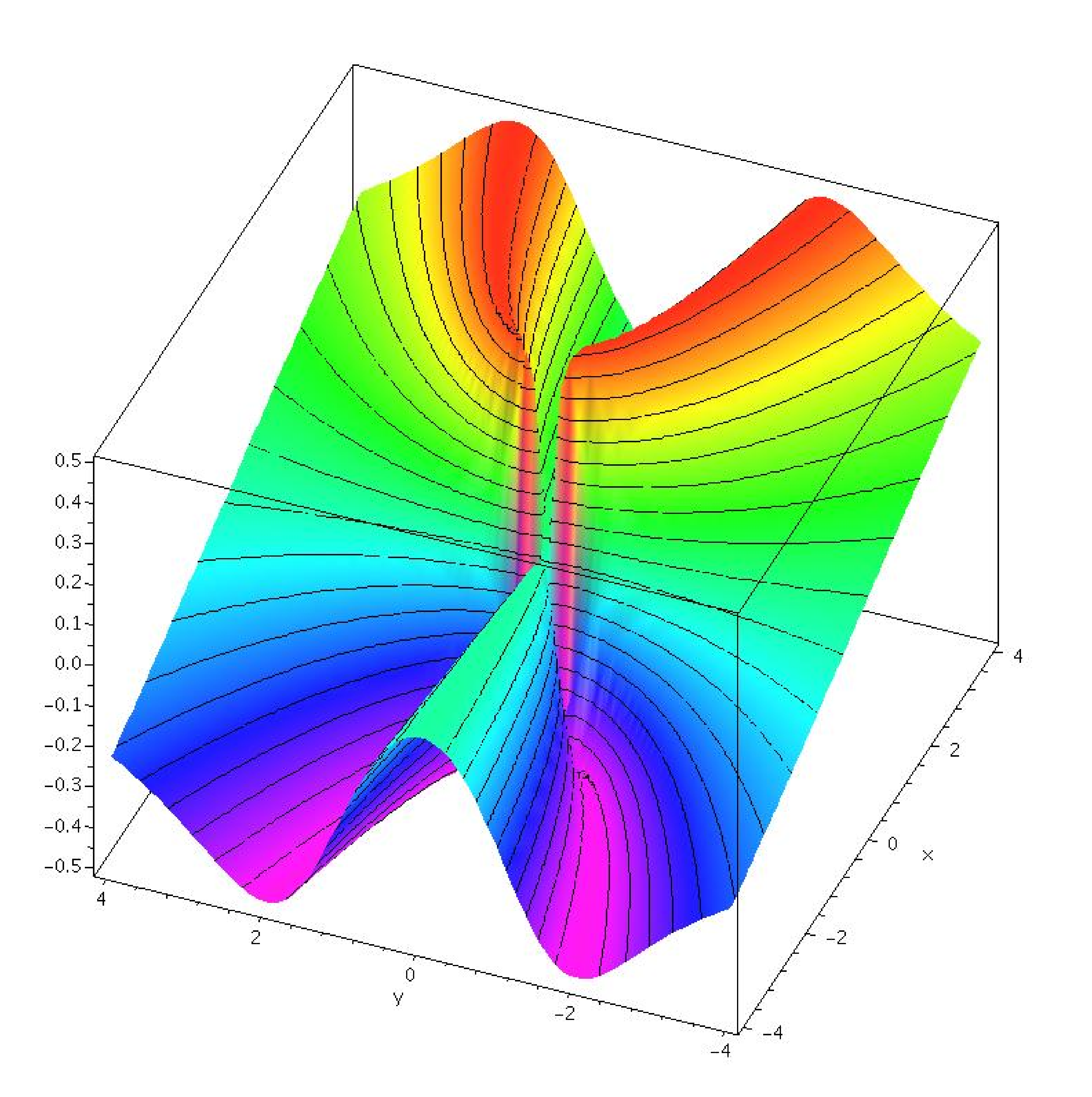


14 2 Limits And Continuity
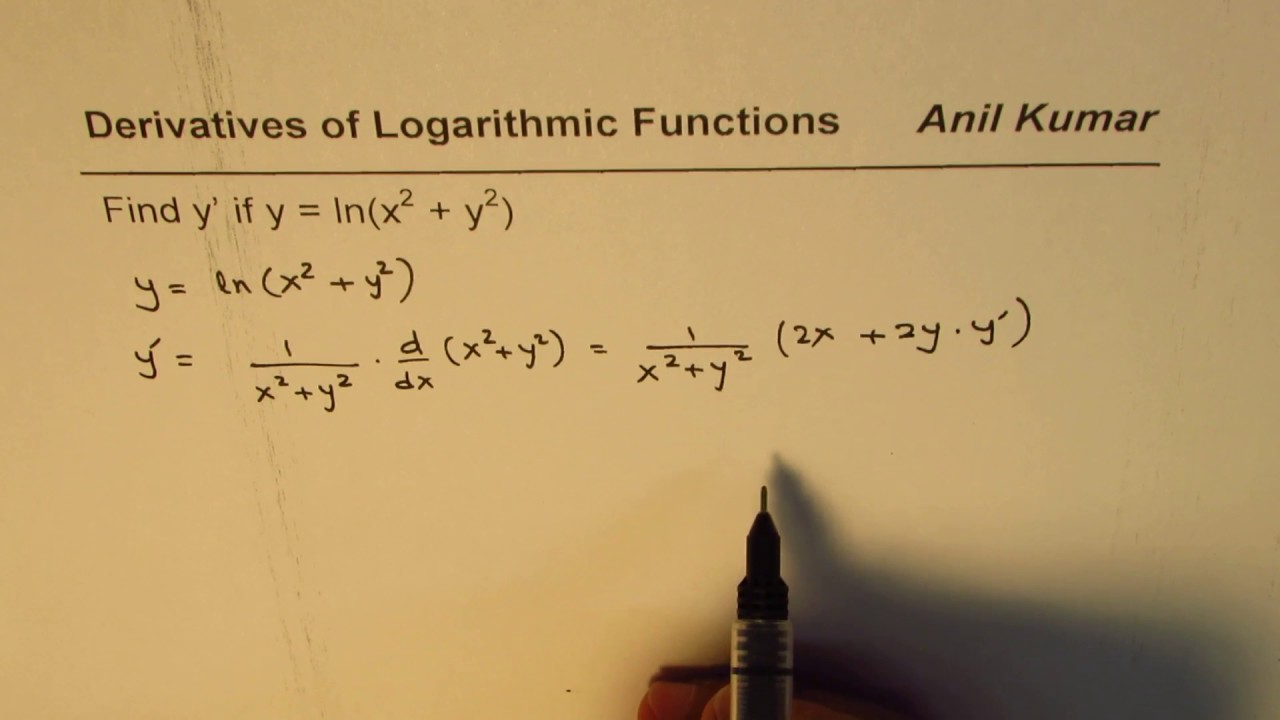


Implicit Derivation Of Logarithmic Function Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿